面试之数组相关
如何判断一个变量是否为数组?
javaScript中有五种方法可以判断一个变量是否为数组,分别是:
- typeof运算符
- instanceof运算符
- constructor属性
- Object.prototype.toString()
- Array.isArray()
- 特性嗅探?
typeof运算符
下表总结了typeof可能的返回值
| 类型 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| Undefined | “undefined” |
| Null | “object” |
| Boolean | “boolean” |
| Number | “number” |
| String | “string” |
| Symbol | “symbol” |
| 宿主对象 | Implementation-dependent |
| 函数对象 | “function” |
| 任何其他对象 | 任何其他对象 |
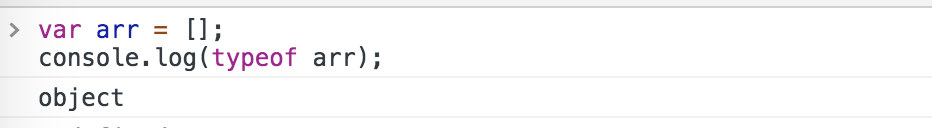
从上表和实际执行结果可以看出,当typeof的参数为null、对象、数组的时候都会返回object,因此用typeof运算符来判断某变量是否为数组是不靠谱的。
instanceof运算符
判断某个构造函数的prototype属性所指向的对象是否存在于object的原型链上
object instanceof constructor
执行结果如下,可以判断出是否是数组1
2var a = [];
console.log(a instanceof Array); //true
constructor属性
原型对象是类的唯一标识,构造函数是类的外在表现 – js权威指南
我们用构造函数来判断类的类型,数组实例的构造函数应该为Array1
2const a1 = [];
console.log(a.constructor === Array); // true
但是对象的constructor是可以修改的,这种方法并不靠谱。
需要注意嵌套 frame 的情况下,instanceof、constructor都会无效
1 | <iframe src='a.htm'></iframe> |
a.htm 代码:1
2
3<script>
window.a = [1, 2, 3];
</script>
我们看到 index.htm 代码中,变量 a 确实是一个数组,但是 a instanceof Array 的结果却是 false。
这是因为每个 frame 都有一套自己的执行环境,跨 frame 实例化的对象彼此不共享原型链。如果打印 a instanceof window.frames[0].Array,那么结果就是 true 了。
Object.prototype.toString()
这个方法也是一些类库进行数组(甚至其他类型)判断的主流方式。看一下测试:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(10)); // [object Number]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call('hello')); // [object String]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(true)); // [object Boolean]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call([])); // [object Array]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call({})); // [object Object]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(function(){})); // [object Function]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(/a/g)); // [object RegExp]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(null)); // [object Null]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined)); // [object Undefined]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(new Date())); // [object Date]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(new Error())); // [object Error]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Symbol())); // [object Symbol]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Math)); // [object Math]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(JSON)); // [object JSON]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(location)); // [object Location]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(history)); // [object History]
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(window)); // [object Window]
function a() {
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(arguments)); // [object Arguments]
}
a();
Array.isArray()
ES5的这个方法,在保证兼容性的前提下可以使用
特性嗅探?
1 | var a = [0, 1, 2]; |
简直不靠谱。
总结
我们来写一个js类型判断函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21// 如果是基本类型,就使用 typeof,引用类型就使用 toString。此外鉴于 typeof 的结果是小写,希望所有的结果都是小写。
var class2type = {};
// 生成class2type映射
"Boolean Number String Function Array Date RegExp Object Error".split(" ").map(function(item, index) {
class2type["[object " + item + "]"] = item.toLowerCase();
})
function type(obj) {
// 在 IE6 中,null 和 undefined 会被 Object.prototype.toString 识别成 [object Object]!
if (obj == null) {
return obj + "";
}
return typeof obj === "object" || typeof obj === "function" ?
class2type[Object.prototype.toString.call(obj)] || "object" :
typeof obj;
}
var isArray = Array.isArray || function( obj ) {
return type(obj) === "array";
}
数组的原生方法有哪些?
| Array.prototype上的方法 | 描述 | 返回值 | 是否改变原数组 | 注意点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| concat() | 方法用于合并两个或多个数组。 | 新数组 | 否 | 返回一个浅拷贝的数组;在嵌套数组合并的时候,之扁平化最外层数组; |
| copyWithin(target[, start[, end]]) | 方法浅复制数组的一部分到同一数组中的另一个位置。 | 改变后的数组 | 是 | 无 |
| entries() | 方法返回一个新的Array Iterator对象,该对象包含数组中每个索引的键/值对 | 新的Array Iterator对象 | 否 | 新Array Iterator对象的原型(proto:Array Iterator)上有一个next方法,可用用于遍历迭代器取得原数组的[key,value] |
| every(callback(元素值,元素的索引,原数组)[, thisArg]) | 方法测试数组的所有元素是否都通过了指定函数的测试 | 布尔值 | 否 | 无 |
| some(callback(element[, index[, array]])[, thisArg]) | 方法测试是否至少有一个元素通过由提供的函数实现的测试 | 布尔值 | 否 | 无 |
| filter() | 方法创建一个新数组, 其包含通过所提供函数实现的测试的所有元素 | 返回通过测试函数为true的元素组成的新数组 | 否 | 无 |
| forEach() | 方法对数组的每个元素执行一次提供的函数 | undefined | 否 | 无 |
| map() | 方法创建一个新数组,其结果是该数组中的每个元素都调用一个提供的函数后返回的结果 | 返回一个由回调函数的返回值组成的新数组 | 否 | 无 |
| fill() | “undefined” | |||
| find() | “undefined” | |||
| findIndex() | “undefined” | |||
| flat() | “undefined” | |||
| flatMap() | “undefined” | |||
| includes() | “undefined” | |||
| indexOf() | “undefined” | |||
| join() | “undefined” | |||
| keys() | “undefined” | |||
| lastIndexOf() | “undefined” | |||
| pop() | “undefined” | |||
| push() | “undefined” | |||
| reduce() | “undefined” | |||
| reduceRight() | “undefined” | |||
| reverse() | “undefined” | |||
| shift() | “undefined” | |||
| slice() | “undefined” | |||
| sort() | “undefined” | |||
| splice() | “undefined” | |||
| toLocaleString() | “undefined” | |||
| toString() | “undefined” | |||
| unshift() | “undefined” | |||
| values() | “undefined” |
| Array.prototype上的属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| constructor | “undefined” |
| length | “undefined” |
如何将一个类数组变量转化为数组?
先来说下什么是类数组
把拥有数值length属性和对应非负整数属性的对象看做一种类型的数组,也就是类数组。
类数组判断的几个点
- 首先typeof返回的是object
- 有数值属性length,且length是有限的非负整数且在0~Math.pow(2, 32)之间
类数组有别于数组的点
- 不具备数组length的一些特性
- 其类属于Object,所以不能从Array.prototype中继承一些有用的方法,但是可以间接地使用Function.call方法调用
- 可以用真正数组遍历的方法来遍历类数组
将类数组变量转化为数组
1 | function likeArray() { |
判断一个对象是否是类数组
1 | var MAX_ARRAY_INDEX = Math.pow(2, 53) - 1; |
说一说ES6中对于数组有哪些扩展?
- 扩展运算符
- Array.from() – 用于将类数组对象和可遍历的对象转为真正的数组
- Array.of() – 用于将一组值,转换为数组
- 实例方法:copyWithin() find() findIndex() fill() entries() keys() values() includes() flat() flatMap()
- 数组空位(ES6 则是明确将空位转为undefined)
你知道Array.prototype的类型是什么吗?
1 | Array.isArray(Array.prototype); // true |
Array.prototype 本身也是一个 Array;
因为 Array.prototype 也是个数组,所以它也有 length 属性,这个值为 0,因为它是个空数组。
求数组最大值
1 | // 原始方法 |
数组去重
1 | // 双循环去重 |
数组乱序
最经典的fiisher-Yates洗牌算法;借助图形来直观的看下: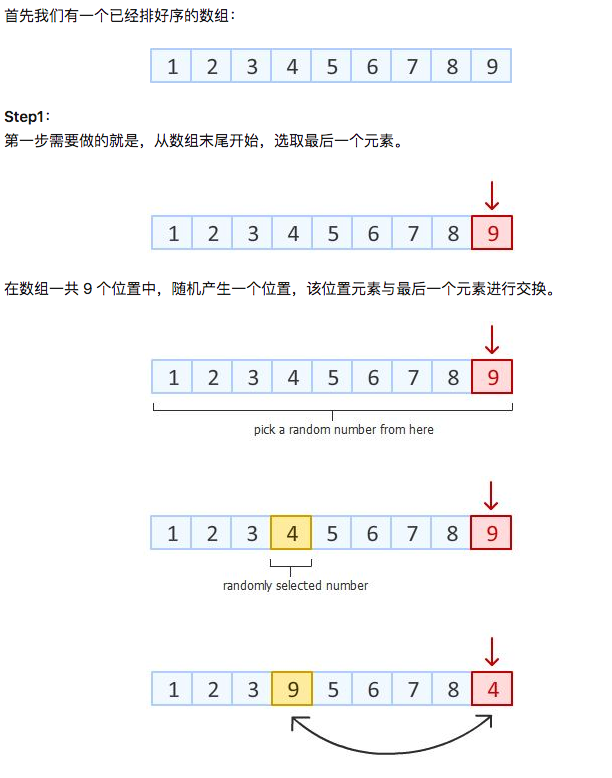
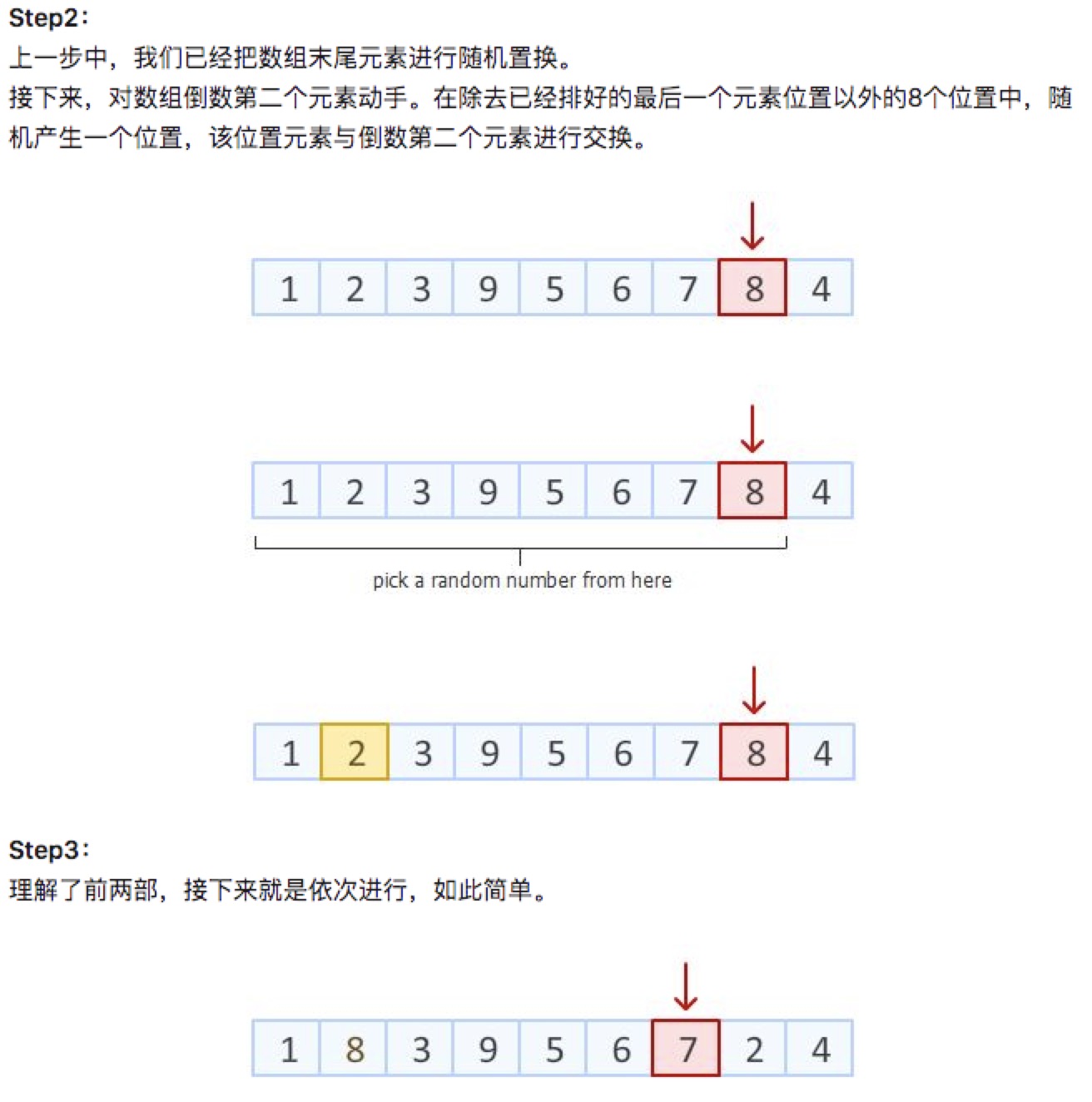
最后的代码实现:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13function shuffle(arr) {
var len = arr.length,
r, t;
while(len) {
r = Math.floor(Math.random()*len--);
t = arr[r];
arr[r] = arr[len];
arr[len] = t;
}
return arr;
}
数组扁平化
1 | // 递归方式处理 |